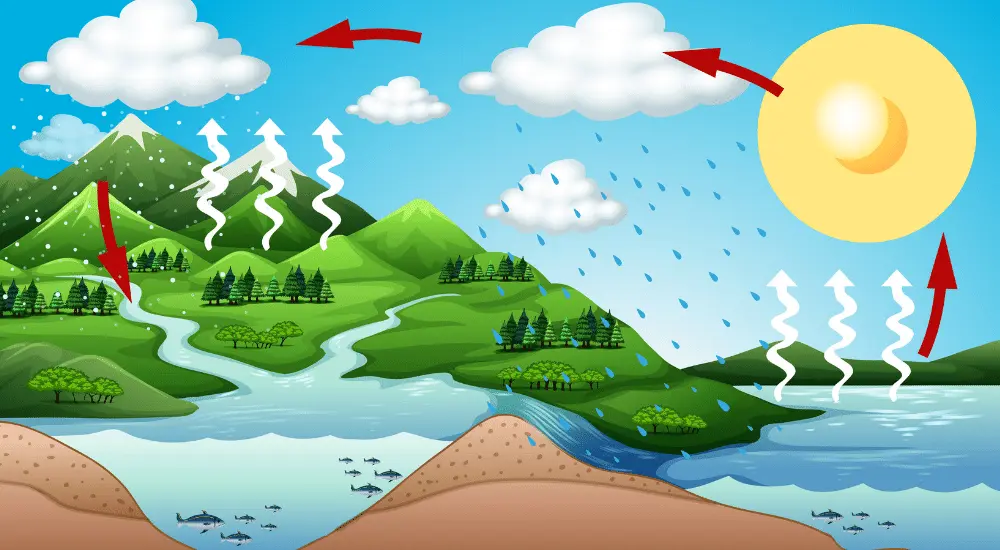
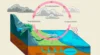
The hydrological cycle, or water cycle, is a remarkable natural process that ensures the continuous circulation of water on our planet. It begins with evaporation, where the sun’s warmth transforms liquid water into vapor. This vapor rises, cools, and condenses into clouds. Next comes precipitation, where clouds release water droplets back to Earth in the form of rain, snow, or hail. Water then replenishes our rivers, lakes, and oceans, sustaining life and ecosystems. Through infiltration, some of it seeps into the ground to replenish underground aquifers. Lastly, plants contribute by releasing water vapor through transpiration. The water cycle, a vital Earth system, underscores the importance of preserving this life-giving resource.
Some important multiple-choice questions related to this topic are listed below. Try to answer these questions after reading enough on this topic. Also, tie your answer to the given one. This practice may help you sharpen your preparation for any competitive exam and increase your knowledge of this topic.
1. What is the primary source of energy that drives the water cycle?
(A) Wind
(B) Solar radiation
(C) Geothermal heat
(D) Tidal forces
(B) Solar radiation
Explanation: Solar radiation from the Sun is the primary source of energy that drives the water cycle. It heats the Earth’s surface, causing water to evaporate from oceans, lakes, and other water bodies, initiating the water cycle.
2. Which process in the water cycle involves the conversion of water vapor into liquid water droplets?
(A) Condensation
(B) Evaporation
(C) Precipitation
(D) Transpiration
(A) Condensation
Explanation: Condensation is the process in which water vapor in the atmosphere cools and changes back into liquid water droplets. This process is responsible for cloud formation.
3. Which of the following is NOT a form of precipitation in the water cycle?
(A) Rain
(B) Snow
(C) Hail
(D) Fog
(D) Fog
Explanation: Fog is not a form of precipitation. Precipitation includes rain, snow, sleet, and hail, which are all forms of water falling from the atmosphere to the Earth’s surface.
4. When water is taken up by plants from the soil and released into the atmosphere through tiny openings in leaves, it is known as:
(a) Evaporation
(B) Infiltration
(C) Transpiration
(D) Condensation
(C) Transpiration
Explanation: Transpiration is the process by which plants absorb water from the soil through their roots and release it into the atmosphere through small openings called stomata in their leaves.
5. Which of the following is a natural reservoir of water in the Earth’s water cycle?
(A) Oceans
(B) Lakes
(C) Rivers
(D) All of the above
(D) All of the above
Explanation: Oceans, lakes, and rivers are all natural reservoirs of water in the Earth’s water cycle. These bodies of water store and release water through various processes in the cycle.
6. What is the process by which water on the surface of the Earth enters the soil and becomes groundwater?
(A) Precipitation
(B) Infiltration
(C) Runoff
(D) Transpiration
(B) Infiltration
Explanation: Infiltration is the process by which water from rainfall or surface water sources penetrates the soil and enters underground aquifers, becoming groundwater.
7. What is the term for the movement of water through underground layers of soil and rock?
(A) Surface runoff
(B) Percolation
(C) Evapotranspiration
(D) Sublimation
(B) Percolation
Explanation: Percolation refers to the movement of water through the pores and spaces in soil and rock beneath the Earth’s surface. It is an important part of groundwater recharge.
8. Which of the following human activities can disrupt the natural hydrological cycle?
(A) Building dams
(B) Planting trees
(C) Recycling paper
(D) Watching TV
(A) Building dams
Explanation: Building dams can disrupt the natural flow of rivers and water bodies, altering the water cycle. Dams can affect downstream water availability and ecosystems.
9. The process of water changing from a gas (water vapor) to a liquid is known as:
(A) Precipitation
(B) Condensation
(C) Infiltration
(D) Transpiration
(B) Condensation
Explanation: Condensation is the phase change from water vapor to liquid water. It occurs when water vapor cools and forms tiny water droplets or ice crystals.
10. What role does the water cycle play in maintaining Earth’s climate and temperature?
(A) It has no impact on climate.
(B) It helps regulate temperature and distribute heat around the planet.
(C) It causes global warming.
(D) It leads to ice ages.
(B) It helps regulate temperature and distribute heat around the planet.
Explanation: The water cycle helps regulate Earth’s temperature by transporting heat from the surface to the atmosphere and distributing it globally. Evaporation and condensation processes are key in this heat transfer, which impacts climate patterns.
11. What is the term for the process by which plants release water vapor into the atmosphere through their leaves?
(A) Precipitation
(B) Evaporation
(C) Transpiration
(D) Infiltration
(C) Transpiration
Explanation: Transpiration is the process by which plants absorb water from the soil through their roots and release it into the atmosphere through tiny openings in their leaves called stomata. It is a key component of the water cycle as it contributes to the moisture in the air.
12. Which of the following is NOT a factor that influences the rate of evaporation?
(A) Temperature
(B) Humidity
C) Wind speed
(D) Atmospheric pressure
(D) Atmospheric pressure
Explanation: Atmospheric pressure is not a factor that directly influences the rate of evaporation. The factors that do influence evaporation include temperature, humidity, wind speed, and surface area.
13. What is the term for the total amount of water vapor present in the air at a given time and place?
(A) Precipitation
(B) Humidity
(C) Transpiration
(d) Runoff
(B) Humidity
Explanation: Humidity is a measure of the amount of water vapor present in the air. It is an important parameter in weather and the water cycle.
14. Which of the following processes in the water cycle involves the conversion of ice directly into water vapor without becoming a liquid first?
(A) Evaporation
(B) Sublimation
(C) Precipitation
(D) Infiltration
(B) Sublimation
Explanation: Sublimation is the process by which ice (solid water) transitions directly into water vapor (gas) without going through the liquid phase. This can occur at cold temperatures and low atmospheric pressures.
15. What is the term for the process by which water flows over the surface of the Earth and into bodies of water like rivers and lakes?
(A) Transpiration
(B) Condensation
(C) Runoff
(D) Infiltration
(C) Runoff
Explanation: Runoff is the process by which water, often from rainfall, flows over the surface of the Earth and eventually enters streams, rivers, lakes, and oceans. It can carry pollutants and sediment with it.









3 Comments
Very very very very good
These questions were helpful to me
Thanks for your feedback. Requesting you to participate in our Quizzes to test your knowledge.