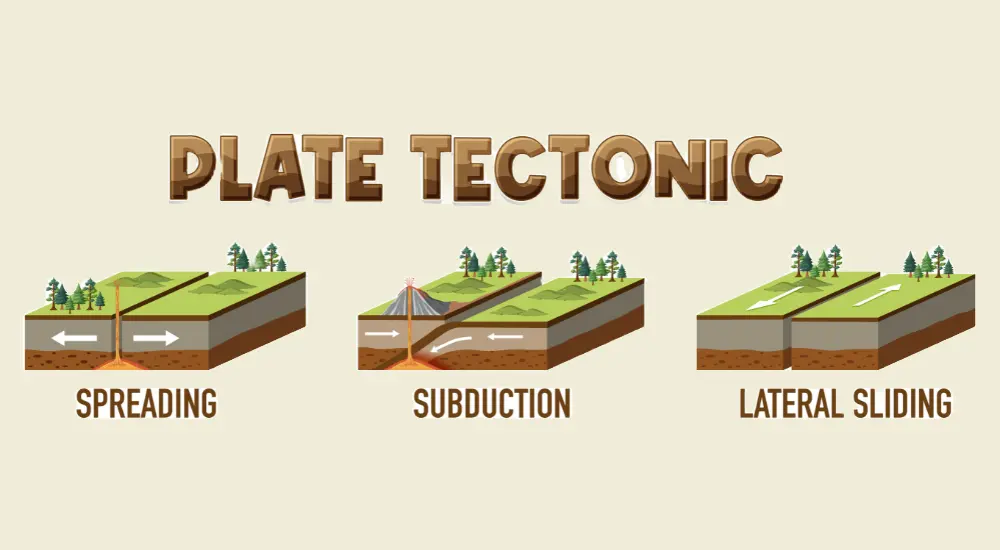
The Plate Tectonic Theory revolutionized our understanding of Earth’s dynamic surface. It proposes that Earth’s lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that constantly move, shaping our planet’s landscapes. These plates interact at boundaries, leading to seismic activity, volcanic eruptions, and mountain formation. The theory also explains continental drift and how oceans open and close over geological time. Understanding plate tectonics helps us predict earthquakes and tsunamis, aiding disaster preparedness. By unlocking the mysteries of this theory, scientists gain invaluable insights into Earth’s evolution and the forces that have shaped our world throughout history.
1. What is the main concept behind plate tectonic theory?
(A) Movement of ocean currents
(B) Shifting of continents
(C) Formation of mountain ranges
(D) Climate change
(B) Shifting of continents
Explanation: Plate Tectonic Theory proposes that Earth’s continents move over time due to the motion of tectonic plates. This movement is known as continental drift.
2. How many major tectonic plates are there on Earth’s surface?
(A) 4
(B) 7
(C) 12
(D) 20
(B) 7
Explanation: Earth’s lithosphere is divided into seven major tectonic plates, such as the Pacific Plate, the Eurasian Plate, and the African Plate.
3. What type of boundary occurs when two tectonic plates move away from each other?
(A) Convergent boundary
(B) Divergent boundary
(C) Transform boundary
(D) Subduction boundary
(B) Divergent boundary
Explanation: A divergent boundary occurs when two tectonic plates move away from each other. It leads to the creation of new crust, typically through volcanic activity, as magma rises to fill the gap.
4. Which type of boundary results in the collision and uplifting of crustal material?
(A) Convergent boundary
(B) Divergent boundary
(C) Transform boundary
(D) Subduction boundary
(A) Convergent boundary
Explanation: A convergent boundary occurs when two tectonic plates collide. This collision can lead to the uplifting of crustal material, creating mountain ranges.
5. What phenomenon is responsible for causing earthquakes along tectonic plate boundaries?
(A) Volcanic eruptions
(B) Plate subduction
(C) Continental drift
(D) Plate divergence
(B) Plate subduction
Explanation: Plate subduction occurs when one tectonic plate is forced beneath another, and it often leads to intense seismic activity and the formation of earthquakes.
6. Which tectonic boundary is associated with the formation of deep ocean trenches?
(A) Divergent boundary
(B) Convergent boundary
(C) Transform boundary
(D) Subduction boundary
(D) Subduction boundary
Explanation: Subduction boundaries are where one tectonic plate moves under another, forming deep ocean trenches in the process.
7. Which scientist is credited with proposing the theory of continental drift, a precursor to Plate Tectonic Theory?
(A) Isaac Newton
(B) Albert Einstein
(C) Charles Darwin
(D) Alfred Wegener
(D) Alfred Wegener
Explanation: Alfred Wegener proposed the theory of continental drift in the early 20th century, suggesting that continents were once connected and have since drifted apart.
8. Which natural feature is formed at a divergent boundary on land?
(A) Mountain ranges
(B) Rift valleys
(C) Ocean trenches
(D) Volcanoes
(B) Rift valleys
Explanation: At divergent boundaries on land, rift valleys are formed as the crust stretches and pulls apart.
9. What do we call the process by which tectonic plates grind past each other horizontally?
(A) Divergence
(B) Convergence
(C) Subduction
(D) Transform faulting
(D) Transform faulting
Explanation: Transform faulting occurs when two tectonic plates slide horizontally past each other along a transform boundary.
10. Which tectonic boundary is responsible for the formation of volcanic island arcs?
(A) Divergent boundary
(B) Convergent boundary
(C) Transform boundary
(D) Subduction boundary
(D) Subduction boundary
Explanation: Subduction boundaries often result in the formation of volcanic island arcs due to the melting of the subducted plate and subsequent volcanic activity.
11. What type of tectonic boundary is responsible for the formation of mid-ocean ridges?
(A) Divergent boundary
(B) Convergent boundary
(C) Transform boundary
(D) Subduction boundary
(A) Divergent boundary
Explanation: Mid-ocean ridges are formed at divergent boundaries in the ocean, where tectonic plates move away from each other, and new oceanic crust is created through volcanic activity.
12. The movement of tectonic plates is primarily driven by:
(A) Wind patterns
(B) Ocean currents
(C) Gravitational forces
(D) Mantle convection
(D) Mantle convection
Explanation: The movement of tectonic plates is mainly driven by mantle convection, where the hot material in the Earth’s mantle rises, cools, and sinks, causing the plates to move.
13. The Himalayan Mountain range was formed as a result of the collision between which two tectonic plates?
(A) Indian Plate and Eurasian Plate
(B) Pacific Plate and North American Plate
(C) South American Plate and African Plate
(D) Nazca Plate and South American Plate
(A) Indian Plate and Eurasian Plate
Explanation: The Himalayan mountain range was formed due to the collision between the Indian Plate and the Eurasian Plate at a convergent boundary.
14. Which phenomenon occurs when one tectonic plate is forced beneath another, creating deep ocean trenches?
(A) Seafloor spreading
(B) Rift valley formation
(C) Subduction
(D) Continental drift
(C) Subduction
Explanation: Subduction occurs when one tectonic plate moves beneath another, leading to the formation of deep ocean trenches.
15. The “Ring of Fire” is a zone characterized by intense tectonic activity, including volcanic eruptions and earthquakes. Which tectonic boundary does it primarily encircle?
(A) Divergent boundaries
(B) Convergent boundaries
(C) Transform boundaries
(D) Subduction boundaries
(B) Convergent boundaries
Explanation: The “Ring of Fire” primarily encircles convergent boundaries around the Pacific Plate, where intense tectonic activity occurs, resulting in volcanic eruptions and earthquakes.