16. What is the term for the angle between the direction of magnetization in a rock and the horizontal plane?
(A) Magnetic inclination
(B) Magnetic declination
(C) Magnetic reversal
(D) Magnetic anomaly
(A) Magnetic inclination
Explanation: Magnetic inclination refers to the angle between the direction of magnetization in a rock and the horizontal plane, providing information about the latitude at which the rock formed.
17. How do scientists determine the geological history of the earth using paleo magnetism?
(A) By measuring the rate of radioactive decay
(B) By analysing the alignment of magnetic minerals
(C) By counting annual growth rings in trees
(D) By studying the composition of fossilized remains
(B) By analysing the alignment of magnetic minerals
Explanation: Scientists determine the geological history of the earth using paleo magnetism by analysing the alignment of magnetic minerals within the rocks relative to the Earth’s magnetic field at the time of their formation.
18. In what type of rocks can paleo magnetism provide evidence of past continental positions?
(A) Sedimentary rocks
(B) Metamorphic rocks
(C) Igneous rocks
(D) Organic rocks
(C) Igneous rocks
Explanation: Paleo magnetism can provide evidence of past continental positions primarily in igneous rocks, which record the orientation of Earth’s magnetic field at the time of their formation and can be used to reconstruct past continental drift.
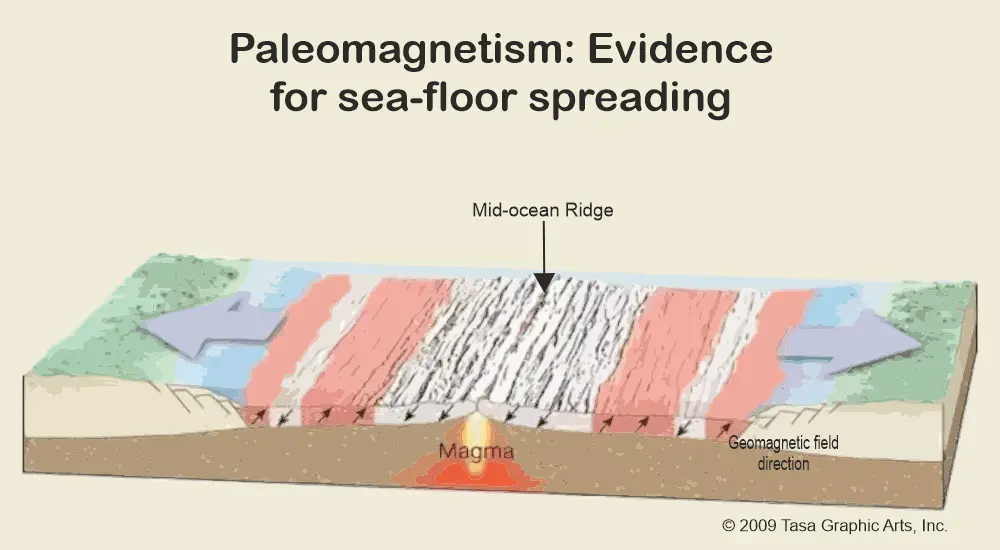
19. How do scientists use paleomagnetic data to study plate tectonics?
(A) By measuring the age of rocks using magnetic properties
(B) By determining the rate of seafloor spreading
(C) By reconstructing past positions of continents
(D) By studying the composition of volcanic gases
(C) By reconstructing past positions of continents
Explanation: Scientists use paleomagnetic data to study plate tectonics by reconstructing past positions of continents based on the orientation of Earth’s magnetic field recorded in rocks, providing evidence of past continental drift.
20. What term describes the alignment of magnetic minerals in rocks with the Earth’s magnetic field at the time of their formation?
(A) Magnetic declination
(B) Magnetic anomaly
(C) Remanence
(D) Magnetic inclination
(C) Remanence
Explanation: Remanence refers to the residual magnetization acquired by rocks during their formation, preserving the alignment of magnetic minerals with the Earth’s magnetic field at that time.
21. Which phenomenon occurs when the magnetic minerals in a rock align with the current magnetic field upon cooling below the Curie temperature?
(A) Magnetic reversal
(B) Magnetic inclination
(C) Thermoremanent magnetization
(D) Isothermal remanent magnetization
(C) Thermoremanent magnetization
Explanation: Thermoremanent magnetization occurs when the magnetic minerals in a rock align with the Earth’s magnetic field upon cooling below the Curie temperature, preserving the direction of the magnetic field at the time of cooling.
22. How do scientists use paleo magnetism to study the past behaviour of the Earth’s magnetic field?
(A) By measuring the intensity of magnetic minerals in rocks
(B) By analysing the alignment of magnetic minerals in rocks
(C) By studying the composition of volcanic gases
(D) By dating the formation of sedimentary rocks
(B) By analysing the alignment of magnetic minerals in rocks
Explanation: Scientists use paleo magnetism to study the past behaviour of the Earth’s magnetic field by analysing the alignment of magnetic minerals in rocks, which record the orientation of the magnetic field at the time of their formation. This provides insights into past changes in the Earth’s magnetic field and its geomagnetic history.