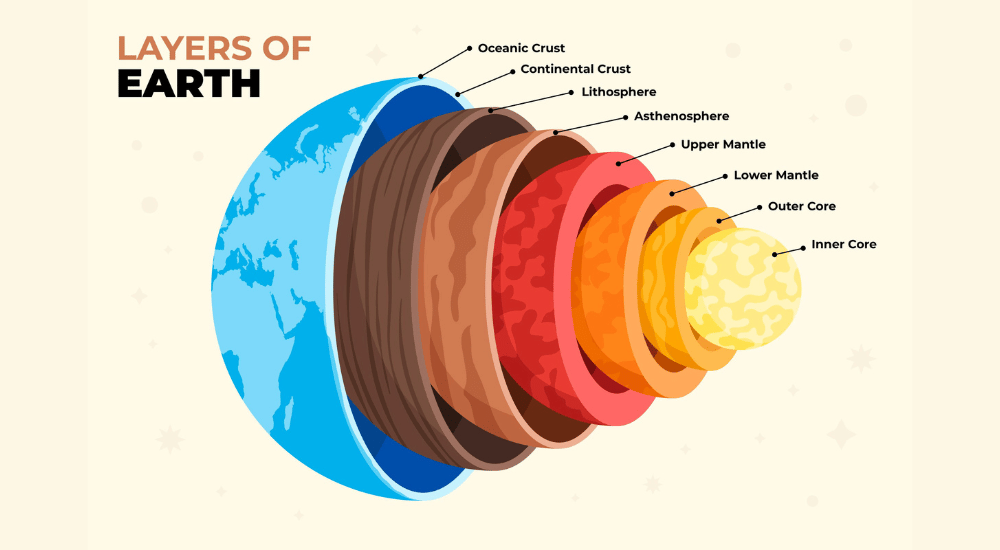
16. Which layer of the Earth is responsible for generating volcanic activity?
(A) Crust
(B) Mantle
(C) Outer core
(D) Inner core
(A) Crust
Explanation: Volcanic activity is primarily associated with the Earth’s crust. Magma, formed by the partial melting of rocks in the mantle, rises to the surface through volcanic vents and erupts as lava during volcanic activity.
17. Which seismic waves cannot travel through liquids?
(A) P-waves
(B) S-waves
(C) Surface waves
(D) Love waves
(B) S-waves
Explanation: S-waves (secondary waves) are shear waves that cannot travel through liquids. They move material perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation and require solid material for transmission.
18. What is the main source of heat in the Earth’s interior?
(A) Solar radiation
(B) Geothermal energy
(C) Nuclear reactions
(D) Frictional heating
(C) Nuclear reactions
Explanation: The main source of heat in the Earth’s interior is the energy generated by nuclear reactions, specifically the decay of radioactive isotopes. This heat contributes to the processes like convection and drives plate tectonics.
19. Which layer of the Earth experiences the highest pressure?
(A) Crust
(B) Mantle
(C) Outer core
(D) Inner core
(D) Inner core
Explanation: The inner core experiences the highest pressure of all the layers of the Earth. The tremendous pressure from the weight of the overlying layers keeps the iron-nickel alloy in the inner core solid despite its high temperature.
20. The lithosphere is divided into several large plates. Approximately how many major tectonic plates are there?
(A) 4
(B) 7
(C) 10
(D) 15
(B) 7
Explanation: The lithosphere is divided into approximately 7 major tectonic plates, including the Eurasian Plate, African Plate, Pacific Plate, North American Plate, South American Plate, Australian Plate, and Antarctic Plate. These plates interact with each other at their boundaries and contribute to the Earth’s geologic activity.